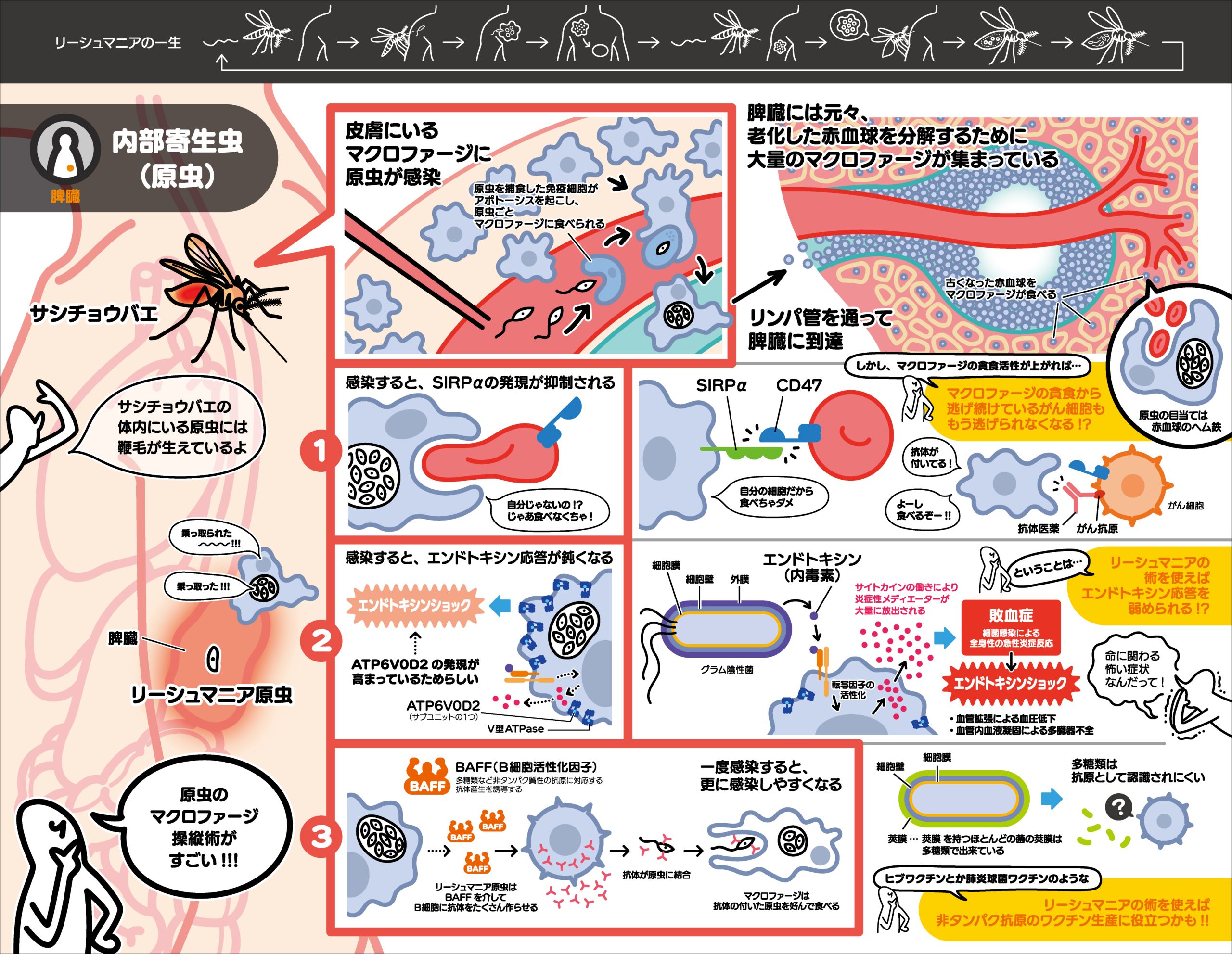
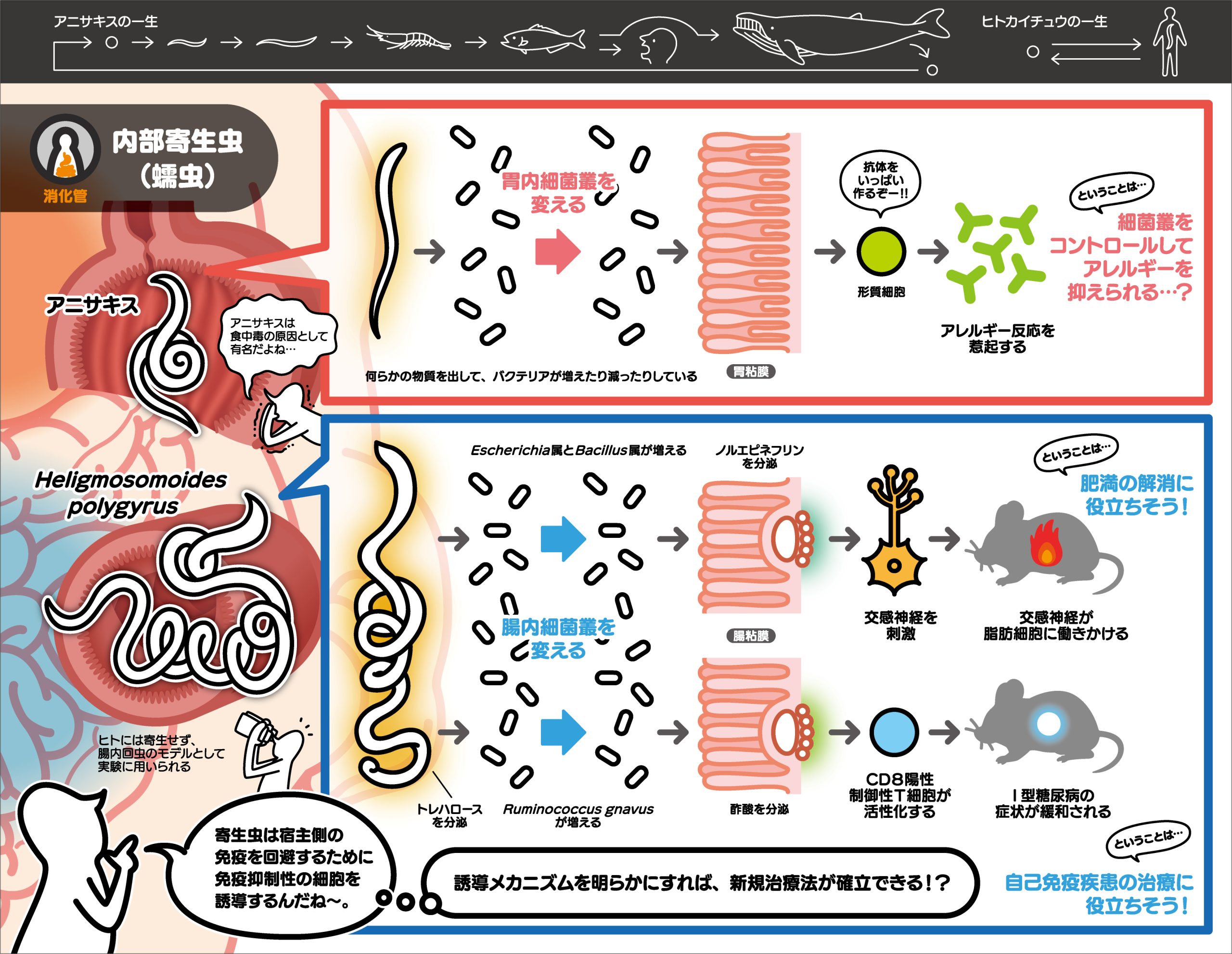
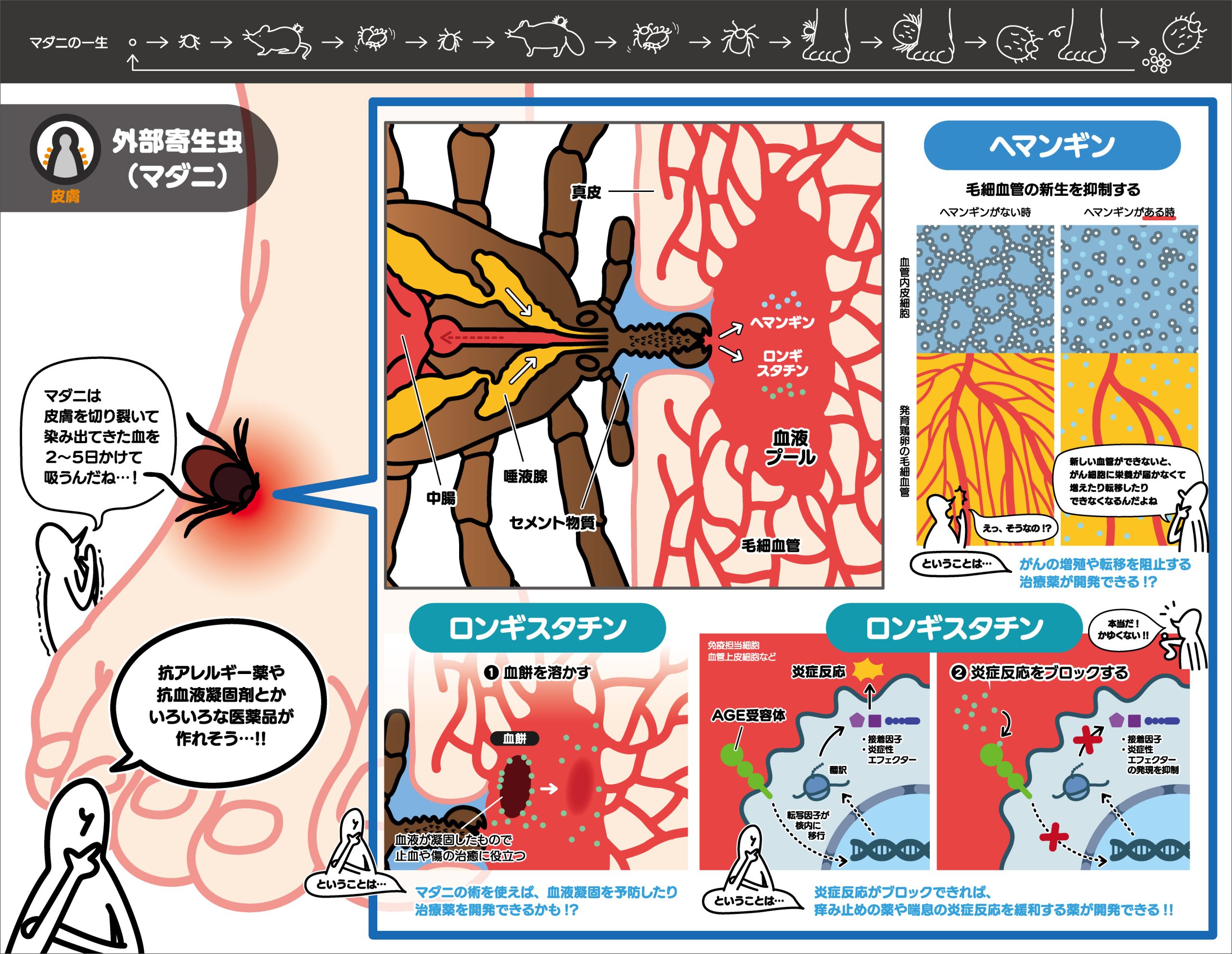
In patients with visceral leishmaniasis, a parasitic disease, macrophages in the bone marrow and lymph nodes become polynucleated and phagocytize their own red blood cells. In this study, we clarified that ATP6V0D2, a component of V-ATPase, is involved in protozoan infection-induced multinucleation. It is expected to be an important step in understanding the macrophage modification mechanism of protozoa.